Thematic Analysis in UX Research: Step-by-Step Guide

- 2024-05-18
Thematic Analysis in UX Research: Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction
Thematic analysis is one of the most popular and flexible methods for analyzing qualitative data in UX research. Whether you're working with user interviews, usability tests, or open-ended survey responses, thematic analysis helps you systematically identify, code, and interpret patterns—called themes—within your data. This guide will show you how to conduct thematic analysis step by step, why it's essential for UX, and how modern tools like Leapfrog can make the process faster, more collaborative, and more insightful.
What is Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method for identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within data. Originally formalized by Braun & Clarke, it's widely used in UX research because of its flexibility and ability to handle large, unstructured datasets. Unlike content analysis, which often quantifies the presence of specific words or concepts, thematic analysis focuses on meaning, context, and the relationships between ideas. This makes it ideal for uncovering deep insights from user interviews, usability studies, and open-ended feedback.
When to Use Thematic Analysis in UX
Thematic analysis is especially valuable in UX research when you need to make sense of complex, qualitative data. It's commonly used for:
- User interviews and focus groups
- Usability test observations
- Open-ended survey responses
- Diary studies and field notes
Whenever your goal is to understand user motivations, pain points, or behaviors in depth, thematic analysis provides a structured approach to move from raw data to actionable insights.
Step-by-Step Guide to Thematic Analysis in UX
A core strength of thematic analysis is its structured, iterative process for moving from raw qualitative data to actionable themes. The following diagram illustrates this journey:
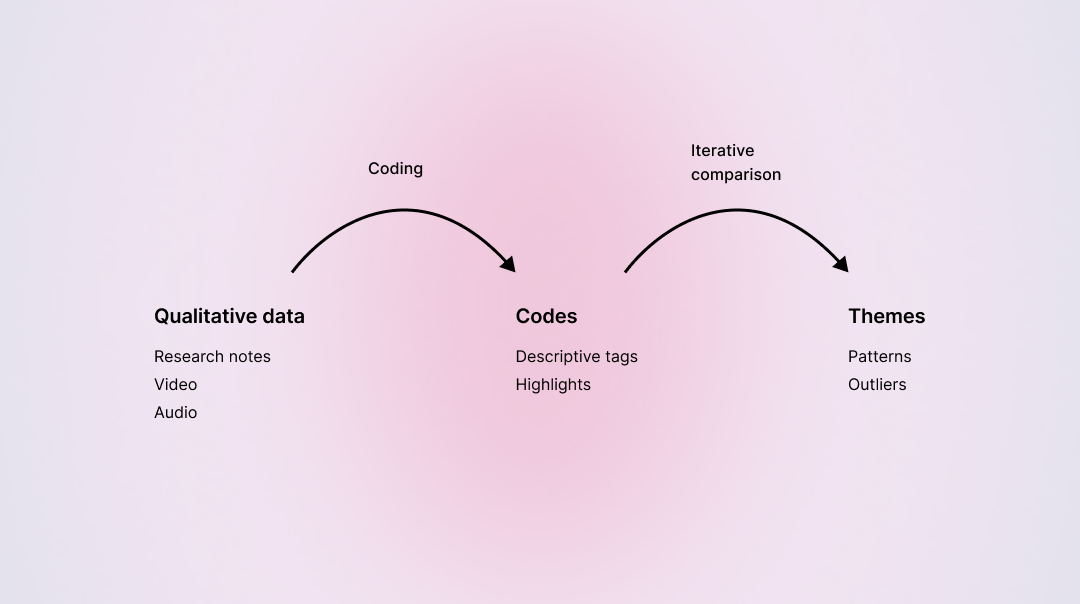 A visual overview of thematic analysis: Qualitative data (such as research notes, video, or audio) is first coded into descriptive tags and highlights. Through iterative comparison, these codes are then grouped into broader themes, revealing patterns and outliers in your data.
A visual overview of thematic analysis: Qualitative data (such as research notes, video, or audio) is first coded into descriptive tags and highlights. Through iterative comparison, these codes are then grouped into broader themes, revealing patterns and outliers in your data.
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Data
Begin by transcribing your interviews or gathering all qualitative data. Read through the material multiple times, making initial notes about interesting points, recurring ideas, or surprising comments. This immersion helps you develop a holistic understanding before coding begins.
Step 2: Generate Initial Codes
Start coding your data by highlighting meaningful segments and assigning short labels (codes) that capture their essence. Codes can be descriptive (e.g., "navigation confusion") or interpretive (e.g., "trust issues"). Coding can be done manually or with the help of qualitative analysis tools. Leapfrog, for example, offers AI-assisted coding to speed up this process and ensure consistency across your dataset.
Step 3: Search for Themes
Review your codes and look for patterns or clusters that suggest broader themes. Group related codes together—this is where affinity mapping or clustering comes in. For instance, codes like "missed notifications," "slow response," and "unclear alerts" might cluster under a theme like "communication breakdown."
Step 4: Review and Refine Themes
Examine your themes in relation to the entire dataset. Are they distinct, meaningful, and supported by enough data? Merge, split, or redefine themes as needed. This iterative process ensures your themes accurately reflect the data and answer your research questions.
Step 5: Define and Name Themes
Clearly define what each theme means and what it includes (and excludes). Give each theme a concise, descriptive name. This step is crucial for clarity and for communicating your findings to stakeholders.
Step 6: Write Up and Visualize Insights
Present your themes with supporting quotes, examples, and visualizations. Use dashboards, charts, or thematic maps to make your findings accessible and actionable. Leapfrog's analytics and visualization features can help you create compelling reports that drive UX decisions.
Practical Example: Thematic Analysis in a UX Project
Imagine you're redesigning a mobile banking app. You conduct 12 user interviews to understand pain points and opportunities. After transcribing and coding the interviews, you notice recurring codes like "login frustration," "unclear error messages," and "security concerns." By clustering these codes, you identify themes such as "onboarding barriers" and "trust and security." Reviewing the data, you refine these themes and support them with direct user quotes. Finally, you present your findings in a report with visualizations, helping your team prioritize improvements for the next design sprint.
Tools for Thematic Analysis in UX
While thematic analysis can be done with sticky notes and spreadsheets, modern tools make the process more efficient and collaborative. Leapfrog stands out for UX research with features like:
- AI-powered coding and clustering to accelerate analysis
- Visual Canvas for affinity mapping and theme development
- Real-time collaboration for team-based research
- Analytics and dashboards for clear, actionable reporting
Other tools like NVivo, Dovetail, and Atlas.ti are also popular, but Leapfrog's intuitive interface and AI-driven workflow are especially suited for fast-paced UX projects.
Best Practices & Common Pitfalls
- Be consistent in coding: Use a clear codebook and calibrate with your team.
- Iterate and review: Thematic analysis is not linear—review and refine your codes and themes as you go.
- Avoid bias: Stay open to unexpected themes and avoid forcing data into preconceived categories.
- Don't overcode: Focus on meaningful patterns, not every minor detail.
- Support themes with evidence: Use direct quotes and examples to back up your findings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is thematic analysis in qualitative research? Thematic analysis is a method for identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within qualitative data. It's widely used in UX research to make sense of user interviews, usability tests, and open-ended feedback.
How do you do thematic analysis step by step? Familiarize yourself with the data, generate initial codes, search for themes, review and refine themes, define and name themes, and write up your findings with supporting evidence and visualizations.
What's the difference between thematic and content analysis? Content analysis often quantifies the presence of specific words or concepts, while thematic analysis focuses on meaning, context, and relationships between ideas.
Can you automate thematic analysis? AI-powered tools like Leapfrog can automate parts of coding and clustering, making thematic analysis faster and more consistent, but human interpretation remains essential.
How do you visualize themes in UX research? Use thematic maps, affinity diagrams, dashboards, and charts to present your themes. Leapfrog's analytics and Canvas features are especially useful for this.
Can you give a thematic analysis example? See the practical example above, where user interview codes are clustered into themes like "onboarding barriers" and "trust and security" to guide a mobile app redesign.
Conclusion
Thematic analysis is a powerful, flexible method for extracting actionable insights from qualitative UX research. By following a structured, step-by-step approach and leveraging modern tools like Leapfrog, you can turn complex user data into clear, compelling themes that drive better design and product decisions.
Ready to elevate your UX research? Try Leapfrog for fast, collaborative, and insightful thematic analysis.